- The nucleus is represented by the atomic symbol
- For individual elements, you have to determine the number of valence electrons, which are represented by the dots around the atomic symbol
- To find the number of valence electrons is simple, look at the group number the element is in and that shows you the number of valence electrons
- There are four orbitals on each side of the nucleus holding a maximum of two electrons
- Each orbital gets 1 electron before they pair up, making a lone pair
Lewis diagrams for compounds and ions
- In covalent compounds, electrons are shared
1. Determine the number of valence electrons for each atom in the molecule, which I explained above
2. Place atoms so that valence electrons are shared to fill each orbital
This example shows the Lewis diagram for NF3
Double and triple bonds
Helpful Hint: Sometimes the only way covalent compounds can fill all their valence levels is if they share more than one electron
Lewis diagrams: Ionic compounds
- In ionic compounds electron transfer from one element to another
- Determine the number of valence electrons on the cation. Move these to the anion
- Draw [ ] around the metal and the non-metal
- Write the charges outside the brackets





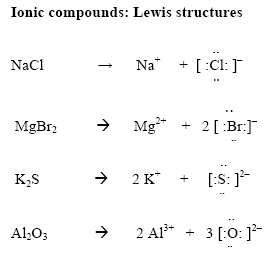
No comments:
Post a Comment